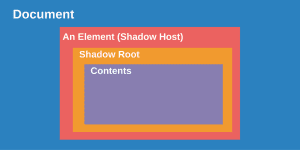
The Shadow DOM is a vital feature in modern web development, enabling developers to encapsulate the internal structure of web components. This encapsulation separates a component’s internal DOM from the global DOM, ensuring styles and scripts don’t interfere with other elements.
Accessing Shadow DOM Elements in JavaScript
To interact with elements inside the Shadow DOM, the component must use mode: ‘open’. This allows direct access to the shadow root and its child elements. Here’s how you can access and style elements within a shadow root:
// Access the shadow root
const shadowRoot = document.querySelector('host-element').shadowRoot;
// Access a child element
const shadowElement = shadowRoot.querySelector('.child-element');
// Apply styling
shadowElement.style.color = 'blue';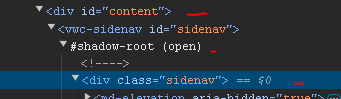
One-Liner for Shadow DOM Manipulation
Streamline your code with a one-liner to access and style elements within the Shadow DOM. For example:
document.querySelector('#content').shadowRoot.querySelector('.sidenav').setAttribute('style', 'padding: 10px');In this example:
• #content is the ID of the host element.
• .sidenav is the class inside the Shadow DOM.
• The setAttribute method applies padding directly to the element.
Why Use Shadow DOM?
1. Isolation: Shadow DOM encapsulates styles and prevents them from conflicting with global styles.
2. Reusability: Components built with Shadow DOM are highly reusable across projects.
3. Flexibility: Accessing and manipulating shadow elements with JavaScript allows dynamic changes without affecting other components.
Best Practices for Styling Shadow DOM
• Use CSS variables to make styling more dynamic.
• Ensure compatibility by gracefully handling cases where the Shadow DOM is in mode: ‘closed’.
• Keep performance in mind when querying elements within the shadow tree.
Unlock the power of the Shadow DOM to create isolated, reusable, and dynamic components. With JavaScript, you can seamlessly access and manipulate shadowed elements to deliver polished user experiences.